· Rajasekhar Gundala · Database · 7 min read
How to deploy MariaDB 11.2.2 using docker compose behind Caddy v2.7.6
MariaDB turns data into structured information in a wide array of applications, ranging from banking to websites. It is an enhanced, drop-in replacement for MySQL.

Previously I deployed MariaDB in docker swarm environment. You can check the article here.
Today I am going to show you how to deploy MariaDB 111.2.2 using docker compose behind Caddy proxy. Here we are not exposing the MariaDB service to the external. It is available only to the internal services or applications.
Lets start with the actual deployment…
MariaDB turns data into structured information in a wide array of applications, ranging from banking to websites. It is an enhanced, drop-in replacement for MySQL.
MariaDB is used because it is fast, scalable and robust, with a rich ecosystem of storage engines, plugins and many other tools make it very versatile for a wide variety of use cases.
Prerequisite
Please make sure you should fulfill the below requirements before proceeding to the actual deployment.
- Ubuntu latest server (any Linux flavor works but I am using Ubuntu here).
- Docker and Docker Compose installed on the Ubuntu Server.
Introduction to MariaDB
MariaDB is one of the most popular database servers in the world. It’s a fork of MySQL, made by the original developers of MySQL.
MariaDB is guaranteed to stay open source. Notable users include Wikipedia, WordPress.com and Google.
MariaDB is developed as open-source software and as a relational database, it provides an SQL interface for accessing data.
The latest versions of MariaDB also include GIS and JSON features.
You can find more about MariaDB here.
Secure MariaDB Environment
MariaDB Docker images have typically offered various ways to set the MySQL root password, where some methods are recommended over others.
Ways to set passwords…
- Specify
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDandMYSQL_PASSWORDin environment variable section in compose file. - Mounting a password file into the container and have
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD,MYSQL_PASSWORD,MYSQL_ROOT_HOST,MYSQL_DATABASEandMYSQL_USERin it. - Specify
MYSQL_RANDOM_ROOT_PASSWORDin environment variable section to have MariaDB generate a random root password. The generated root password will be printed to stdout (GENERATED ROOT PASSWORD: .....). Recommended method - Docker Secrets – Secrets are securely stored in an encrypted Raft log and replicated to other nodes in the cluster. Recommended method
We use Docker Secrets method for passing required password values to MariaDB Container.
Specifying MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD in environment variable is the least secure option. The environment variables are exposed to both the host system and to the container itself, leaving the password at very high risk of exposure.
Mounting a password file will avoid some of the exposure, but the file would still have to be stored on the host system. Not really ideal.
Docker introduced a new mechanism for managing sensitive data with Docker Secrets in version 1.13. Click here to get an overview of it.
Setting up containers with secrets in Docker Compose is straightforward. We’ll specify our secrets in the environment variable section, and tell MariaDB to use those secrets after the container starts.
MariaDB Custom Configuration File
The startup configuration is specified in the file /etc/mysql/my.cnf, and that file in turn includes any files found in the /etc/mysql/conf.d directory that end with .cnf. Settings in files in this directory will augment and/or override settings in /etc/mysql/my.cnf. If you want to use a customized MySQL configuration, you can create your alternative configuration file in a directory on the host machine and then mount that directory location as /etc/mysql/conf.d inside the mariadb container.
If
/my/custom/config-file.cnfis the path and name of your custom configuration file, you can start yourmariadbcontainer with the directory path of the custom config file.
You have to mount only the directory path of the custom config file like the command below:
version: "3.7"
services:
mariadb:
image: mariadb:latest
volumes:
- /my/custom:/etc/mysql/conf.d
This will start a new container
mariadbwhere the MariaDB instance uses the combined startup settings from/etc/mysql/my.cnfand/etc/mysql/conf.d/config-file.cnfwith settings from the latter taking precedence.
MariaDB without Configuration File
Many configuration options can be passed as flags to mysqld. This will give you the flexibility to customize the container without needing a cnf file.
For example, if you want to change the default encoding and collation for all tables to use UTF-8 (
utf8mb4). Alsowait_timeout,interactive_timeoutandmax_allowed_packetsettings for the container. Just include the values incommandkey as described in below code:
version: "3.7"
services:
mariadb:
image: mariadb:latest
command: "mariadb", "--character-set-server=utf8mb4", "--collation-server=utf8mb4_unicode_ci", "--wait_timeout=28800", "--interactive_timeout=28800", "--max_allowed_packet=256M"]
Please check mariadb docker hub for more configuration options.
Prepare MariaDB Environment
Let’s start creating passwords for MariaDB Container using the Docker Secrets method.
Create wp_db_password.txt and mysql_root_password.txt text files with your secrets in the directory.
sudo nano wp_db_password.txt
sudo nano mysql_root_password.txt
I am going to persistent /var/lib/mysql of Maria DB for disorder recovery.
Create folder in /opt directory to persistent MariaDB data folder, /var/lib/mysql
cd /opt
sudo mkdir -p mariadata
Prepare Docker Compose File
Now it’s time to create a docker compose file that contains the Caddy Reverse Proxy service, MariaDB service (you can add more services later that depends on MariaDB) in /opt directory. docker compose is the configuration file in .yml (Yet Another Markup Language).
Create a docker network caddy, we will use it to expose application containers or internal services to outside world.
docker network create caddy
We will use another network (bridge network)
inetto connect MariaDB service securely with out exposing it to external.
Use the below commands to create the configuration file,
cd /opt
sudo touch docker-compose.yml
Open docker-compose.yml with nano editor using sudo nano docker-compose.yml
Copy and paste the below code in the docker-compose.yml configuration file.
Here is the full docker-compose file.
version: "3.7"
services:
maria:
image: mariadb:latest
container_name: maria
restart: unless-stopped
depends_on:
caddy:
condition: service_started
volumes:
- ./mariadata:/var/lib/mysql
secrets:
- mysql_user
- mysql_database
- mysql_db_password
- mysql_root_password
environment:
- MYSQL_USER_FILE=/run/secrets/mysql_user
- MYSQL_DATABASE_FILE=/run/secrets/mysql_database
- MYSQL_PASSWORD_FILE=/run/secrets/mysql_db_password
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD_FILE=/run/secrets/mysql_root_password
command: ["--wait_timeout=28800", "--interactive_timeout=28800", "--max_allowed_packet=256M", "--transaction-isolation=READ-COMMITTED", "--binlog-format=ROW"]
networks:
- inet
healthcheck:
test: ['CMD', '/usr/local/bin/healthcheck.sh', '--innodb_initialized']
start_period: 5s
timeout: 5s
interval: 5s
retries: 5
caddy:
image: rajaseg/caddy
restart: unless-stopped
container_name: caddy
ports:
- target: 80
published: 80
mode: host
- target: 443
published: 443
mode: host
- target: 443
published: 443
mode: host
protocol: udp
- target: 2019
published: 2019
mode: host
networks:
- caddy
- inet
volumes:
- ./Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile
- ./caddydata:/data
- ./caddyconfig:/config
- ./caddylogs:/var/log/caddy
- ./mariadata:/var/lib/mysql
secrets:
mysql_user:
file: ./mysql_user.txt
mysql_database:
file: ./mysql_database.txt
mysql_root_password:
file: ./mysql_root_password.txt
mysql_db_password:
file: ./mysql_db_password.txt
volumes:
caddydata:
caddyconfig:
caddylogs:
mariadata:
networks:
caddy:
external: true
inet:
driver: bridge
Lets discuss about some of the configuration options above.
depends_on
depends_on expresses startup and shutdown dependencies between services.
short syntax
The short syntax variant only specifies service names of the dependencies. Service dependencies cause the following behaviors:
- Compose creates services in dependency order. In the above scenario,
caddyis created beforemaria. - Compose removes services in dependency order. In the above scenario,
mariais removed beforecaddy.
Compose guarantees dependency services have been started before starting a dependent service. Compose waits for dependency services to be ready before starting a dependent service.
restart_policy is to configure whether and how to restart containers when they exit.
condition: One ofnone,on-failureorany. Default is any*.*
Deploy the Docker Compose
Now it’s time to deploy our docker-compose file above using the below command
docker compose up -d
Check the status of the services or containers using docker ps
Create Databases
Type docker ps on server to get the running containers. The out should look like below.
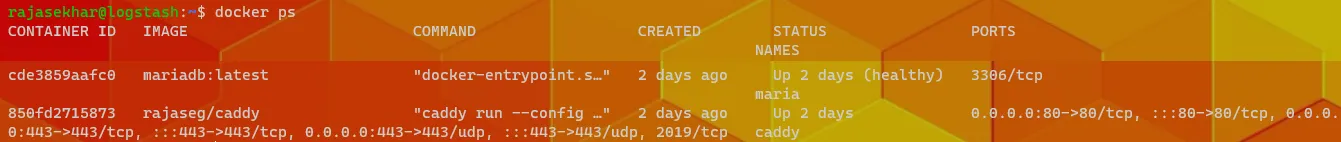
Note down CONTAINER ID of MariaDB from the above command.
Login to MariaDB Container.
Type docker exec -it CONTAINER ID bash to log into MariaDB Container.
After logging into the container, type mariadb -u root -p to go to the MariaDB admin console.
Enter root password here, whatever you created using the Docker Secrets method in Prepare Environment section of this article.
Just type SHOW DATABASES to see all the databases in our MariaDB Container.
By default the container should create one database that was specified in the configuration file,
testdbhere.
We can create databases using CREATE DATABASE database name;
We will be using the databases for applications we are going to deploy soon.
Delete database using DROP database name;
Please watch the below video for MariaDB Installation in Docker Swarm
https://www.youtube.com/embed/NUcDn3MxJ1c?feature=oembed
I hope you enjoyed this post. Please share your thoughts or feedback on it by commenting.
Stay tuned for other deployments 🙂