· Rajasekhar Gundala · Database · 6 min read
How to deploy MongoDB 4.4.22 in docker swarm behind Traefik v2.0
MongoDB is a NoSQL database program and uses JSON-like documents with schema. MongoDB is developed by MongoDB Inc, and licensed under the Server Side Public License (SSPL).

MongoDB is a document database with the scalability and flexibility that you want with the querying and indexing that you need.
MongoDB is a NoSQL database program and uses JSON-like documents with schema. MongoDB is developed by MongoDB Inc, and licensed under the Server Side Public License (SSPL).
In this post, I am going to show you how to deploy MongoDB 4.2.2 in Docker Swarm Cluster using docker compose{.rank-math-link}.
Rocket.Chat (free, open-source enterprise team chat) and Wekan (open source Kanban) rely on MongoDB database server. You’ll have to get MongoDB installed and configured before continuing to install them.
Also, it is recommended to use the MongoDB Replica Set{.rank-math-link} to improve the performance of Rocket.Chat and Wekan via Meteor Oplog tailing.
Please make sure you should fulfill the below requirements before proceeding to the actual deployment.
Docker Swarm Cluster{.rank-math-link} with GlusterFS as persistent tool.
Traefik{.rank-math-link} as reverse proxy to expose micro-services to external.
Introduction to MongoDB
MongoDB is a document database with the scalability and flexibility that you want with the querying and indexing that you need.
MongoDB is a NoSQL database program and uses JSON-like documents with schema. MongoDB is developed by MongoDB Inc, and licensed under the Server Side Public License (SSPL) .
If you want to learn more about MongoDB, go through the official page and Wikipedia
MongoDB 4.4.22 Features
MongoDB stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents, meaning fields can vary from document to document and data structure can be changed over time.
The document model maps to the objects in your application code, making data easy to work with
Ad hoc queries, indexing, and real time aggregation provide powerful ways to access and analyze your data
MongoDB is a distributed database at its core, so high availability, horizontal scaling, and geographic distribution are built in and easy to use
MongoDB is free to use. Versions released prior to October 16, 2018 are published under the AGPL. All versions released after October 16, 2018, including patch fixes for prior versions, are published under the Server Side Public License (SSPL) v1.
MongoDB is used by the City of Chicago, Codecademy, Google Search, Foursquare, IBM, Orange S.A., The Gap, Inc., Uber, Coinbase, Sega, Barclays, HSBC, eBay, Cisco, Bosch and Urban Outfitters.
Configure MongoDB
The startup configuration is specified in the file etc/mongo/mongod.conf and that file, in turn, includes any files found in the /etc/mongo directory that end with .cnf. Settings in files in this directory will augment and/or override settings in /my/custom/mongod.cnf. If you want to use a customized MongoDB configuration, you can create your alternative configuration file in a directory on the host machine and then mount that directory location as /etc/mongo/mongod.cnf inside the MongoDB container.
If
/my/custom/mongod.confis the path and name of your custom configuration file, you can start yourmongodbcontainer with the directory path of the custom config file.
You have to mount only the directory path of the custom config file like the command below:
version: "3.7"
services:
mongo:
image: mongo
volumes:
- /my/custom:/etc/mongoThis will start a new container
mongodbwhere the MongoDB instance uses the combined startup settings from/my/custom/mongod.cnfand/etc/mongo/mongod.cnfwith settings from the latter taking precedence.
MongoDB without Configuration File (.cnf)
Many configuration options can be passed as flags to mongodb. This will give you the flexibility to customize the container without needing a cnf file.
For example, if you want to reduce disk space that each binary ~bin.mongod instance uses, use oplogSize
If you want to change the default storage engine (Rocket Chat recommends MMAPv1, we can specify
--storageEngine=mmapv1to change default storage from WiredTiger to MMAPv1.
From MongoDB version 4.0, the default storage engine is WiredTiger. If you want to use it, no need to specify it in the command
And also we can specify replica set without configuration file using command in docker swarm configuration.
version: "3.7"
services:
mongo:
image: mongo
command: 'mongod --oplogSize 128 --replSet rs0 ----storageEngine=mmapv1'Please check mongodb docker hub for more configuration options.
Prepare MongoDB Environment
Let’s start creating passwords for MongoDB Container using the Docker Secrets method.
echo "{password}" | docker secret create mongodb_root_passwordWe will use the private docker network we created previously for deploying the MariaDB container.
Create 2 folders in /mnt the directory to persistent MongoDB data folder, /data/db and also for dump folder, /dump
cd /mntsudo mkdir -p mongodbsudo mkdir -p mongodumpPlease go through the below video to i
Please find below video for installing GlusterFS in Docker Swarm for data persistence
GlusterFS Replicated Volume in Docker Swarm
MongoDB Docker Compose
I am going to use docker compose to prepare environment file for deploying WordPress. The compose file is known as YAML ( YAML stands for YAML Ain’t Markup Language) and has extension .yml or .yaml
Now it’s time to create a folder, mongo in /opt directory to place docker-compose configuration file, i.e, mongo.yml file for MongoDB.
Use the below commands to create the folder.
cd /optsudo mkdir -p mongocd mongosudo touch mongo.ymlOpen mongo.yml with nano editor using sudo nano mongo.yml
Copy and paste the below code into it.
Here is the docker compose file for MongoDB.
version: "3.7"
services:
mongo:
image: mongo
volumes:
- /mnt/mongodb:/data/db
- /mnt/mongodump:/dump
command: 'mongod --oplogSize 128 --replSet rs0'
secrets:
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD
environment:
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=user
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD_FILE=/run/secrets/mongodb_root_password
networks:
- proxy
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
secrets:
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD:
external: true
volumes:
mongodb:
driver: "local"
mongodump:
driver: "local"
networks:
proxy:
external: trueDeploy MongoDB using Docker Compose
Now it’s time to deploy our docker-compose file above, mongo.yml using the below command
docker stack deploy --compose-file mongo.yml mongoYou can give it any name for the stack. I just named it as
mongo
We can check the status of the stack by using docker stack ps mongo
Prepare MongoDB Replica Set Environment
It is not good idea to have mongo and mongo replica set services in the same configuration file. If we deploy both the services, the replica set or mongodb would fail. I faced the problem and that’s why I decided to deploy them separately.
Let’s prepare the environment for the replica set.
Use the below commands to create a folder to store docker-compose configuration file for the replica set.
cd /optsudo mkdir -p mongoinitcd mongoinitsudo touch mongoinit.ymlOpen mongoinit.yml with nano editor.
sudo nano mongoinit.ymlCopy and paste the below code on it.
MongoDB Replica Set Docker Compose
Here is the configuration file(.yml) for MongoDB Replica Set.
version: "3.7"
services:
mongo-init-replica:
image: mongo
command: 'mongo mongo/rocketchat --eval "rs.initiate({ _id: ''rs0'', members: [ { _id: 0, host: ''127.0.0.1:27017'' } ]})"'
depends_on:
- mongo
networks:
- proxy
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
networks:
proxy:
external: trueIn the configuration file, I am creating the database for Rocket Chat and initiating MongoDB Replica Set
Deploy / Initiate MongoDB Replica Set using Docker Compose
Now it’s time to deploy our docker-compose file above, mongoinit.yml using the below command
docker stack deploy --compose-file mongoinit.yml mongoinitYou can give it any name for the stack. I just named it as
mongoinit
We can check the status of the stack by using docker stack ps mongoinit
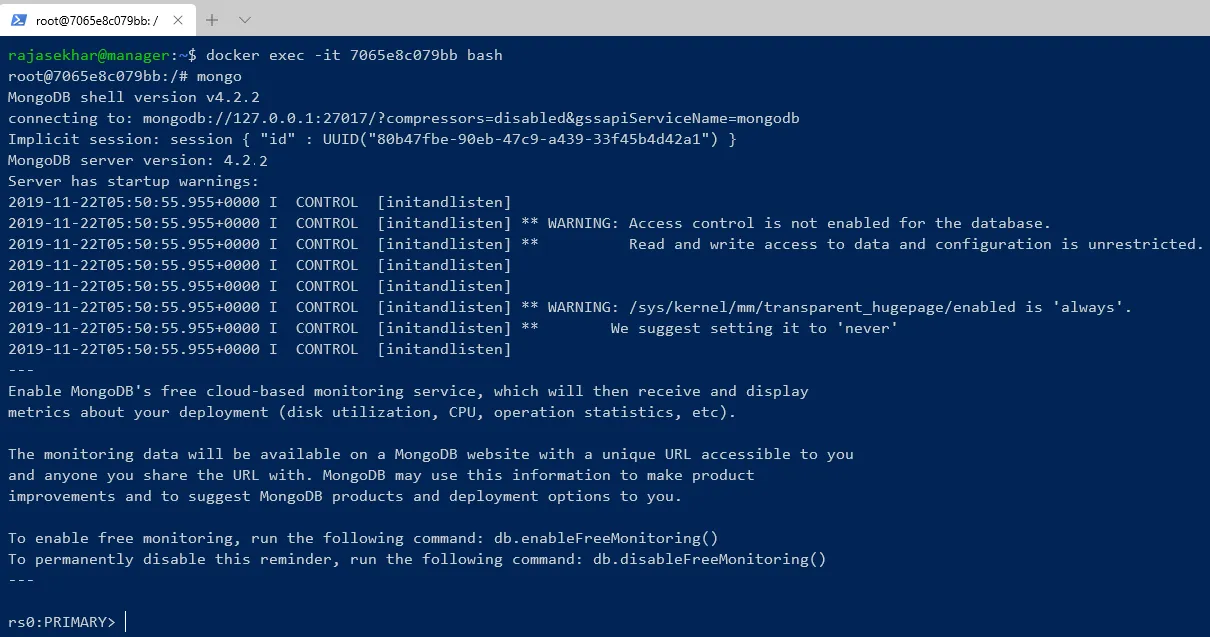
Login to MongoDB Docker Container
Type docker ps on master node to get the running containers on it. The out should look like below.
Note down CONTAINER ID of MariaDB from the above command.
Type docker exec -it CONTAINER ID bash to log into MariaDB Container.
Next post I will deploy Rocket Chat, Team Collaboration software using MongoDB. Stay tuned… 🙂